
Okay, so first, let us discuss two most pivotal concepts for counting: Now, in this video we will look at the first four rules and tackle the remaining counting principle in the next few lessons. The one that is most closely associated with the title of “fundamental counting principle” is the multiplication rule, where if there are p ways to do one task and q ways to another task, then there are pxq ways to do both. While there are five basic counting principles: addition, multiplication, subtraction, cardinality (principle of inclusion-exclusion), and division. The Fundamental Counting Principle, sometimes referred to as the fundamental counting rule, is a way to figure out the number of possible outcomes for a given situation. In this lesson, we will focus on enumeration, or counting objects or elements, that contain specific properties. While you may have already studied these topics in Algebra, the next three lessons along with the pigeonhole principle and binomial theorem, will highlight fundamental concepts of counting and focus on the more challenging aspects of advanced counting. Combinatorics studies combinations, permutations, and enumerations of sets of elements. In fact, an entire branch of mathematics is devoted to the study of counting, and it’s called combinatorics. If we have a set of n objects and we want to choose r objects from the set in order, we write P\left(n,r\right).Jenn, Founder Calcworkshop ®, 15+ Years Experience (Licensed & Certified Teacher) Before we learn the formula, let’s look at two common notations for permutations. Fortunately, we can solve these problems using a formula. The number of permutations of n distinct objects can always be found by n!.įinding the Number of Permutations of n Distinct Objects Using a Formulaįor some permutation problems, it is inconvenient to use the Multiplication Principle because there are so many numbers to multiply. Note that in part c, we found there were 9! ways for 9 people to line up. There are 362,880 possible permutations for the swimmers to line up. There are 9 choices for the first spot, then 8 for the second, 7 for the third, 6 for the fourth, and so on until only 1 person remains for the last spot.

The company that sells customizable cases offers cases for tablets and smartphones. Permutations Using the Addition Principle We will examine this type of mathematics in this section. Other applications of counting include secure passwords, horse racing outcomes, and college scheduling choices. There is a branch of mathematics devoted to the study of counting problems such as this one. We encounter a wide variety of counting problems every day. Counting the possibilities is challenging! The company is working with an agency to develop a marketing campaign with a focus on the huge number of options they offer. The customer can choose the order of the images and the letters in the monogram. A customer can choose not to personalize or could choose to have one, two, or three images or a monogram.

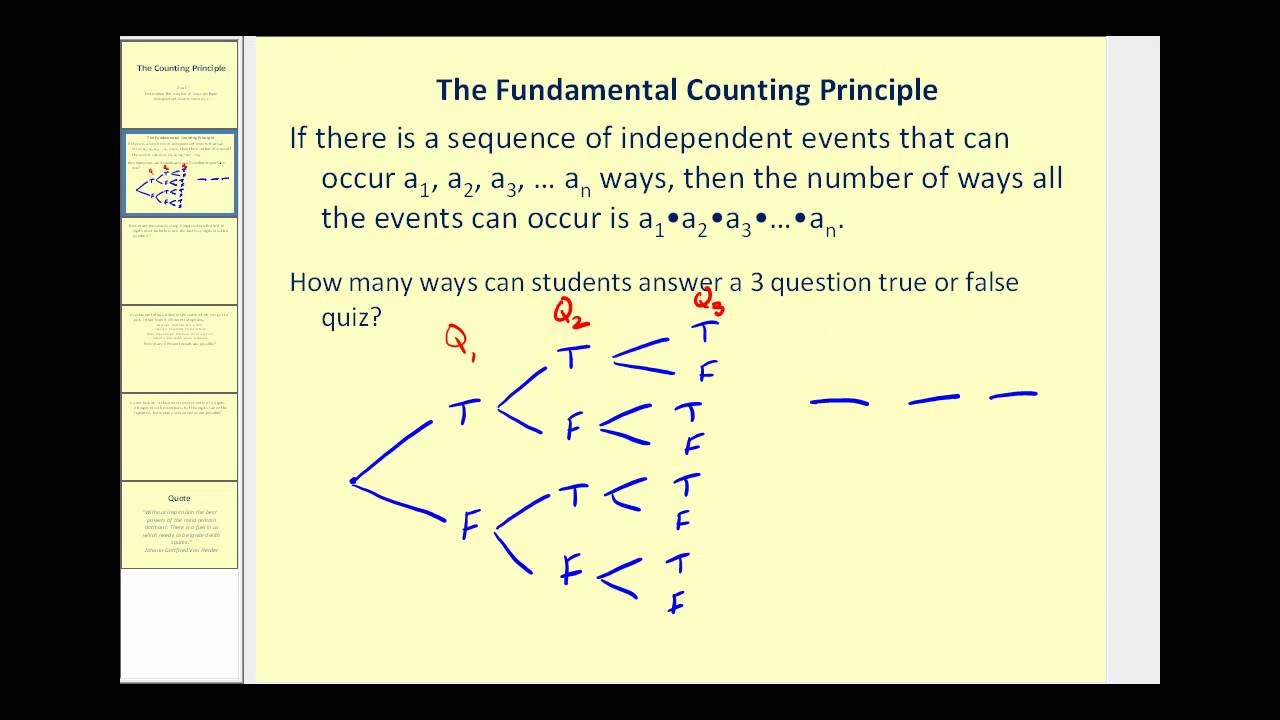
Each case comes in a variety of colors and can be personalized for an additional fee with images or a monogram. Solve counting problems using permutations involving n non-distinct objects.Ī new company sells customizable cases for tablets and smartphones.
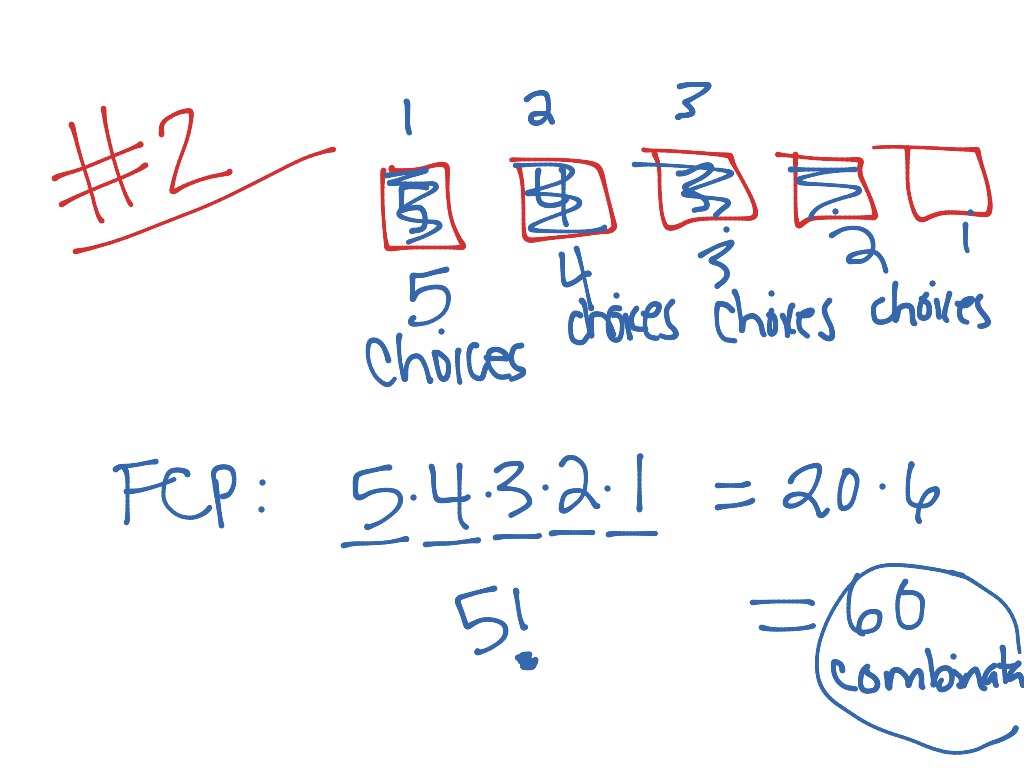


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
